Skin aging and various skin problems arise from a combination of internal and external factors that gradually alter the skin’s structure and appearance. These changes not only affect facial aesthetics but can also impact overall skin health and self-confidence. Skin rejuvenation techniques, such as laser therapy, filler injections, microneedling, and non-invasive treatments, can effectively address these issues.
Natural Aging Process
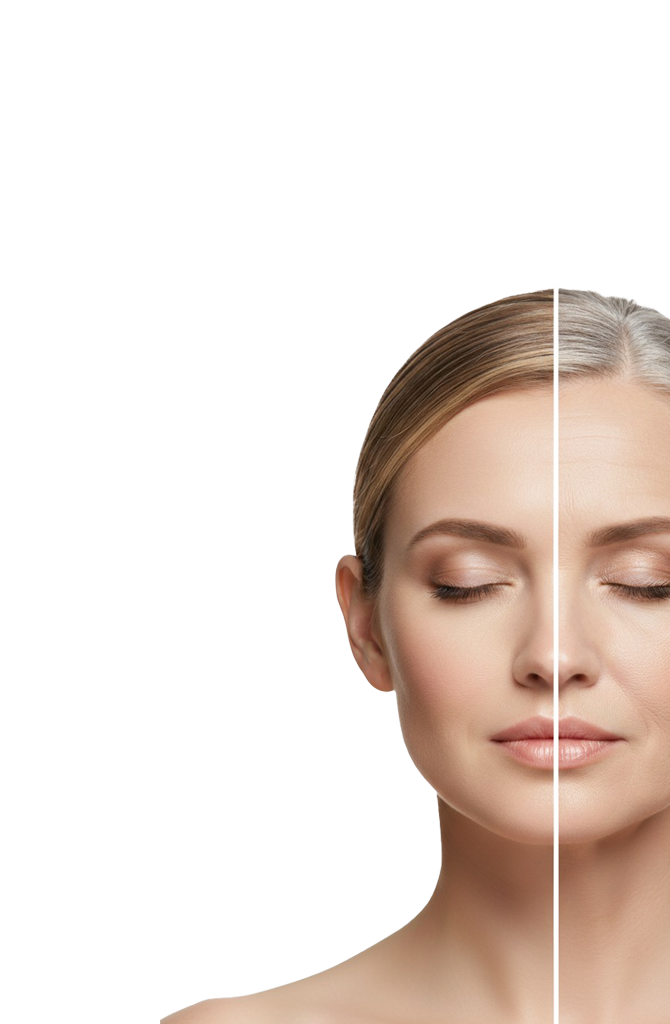
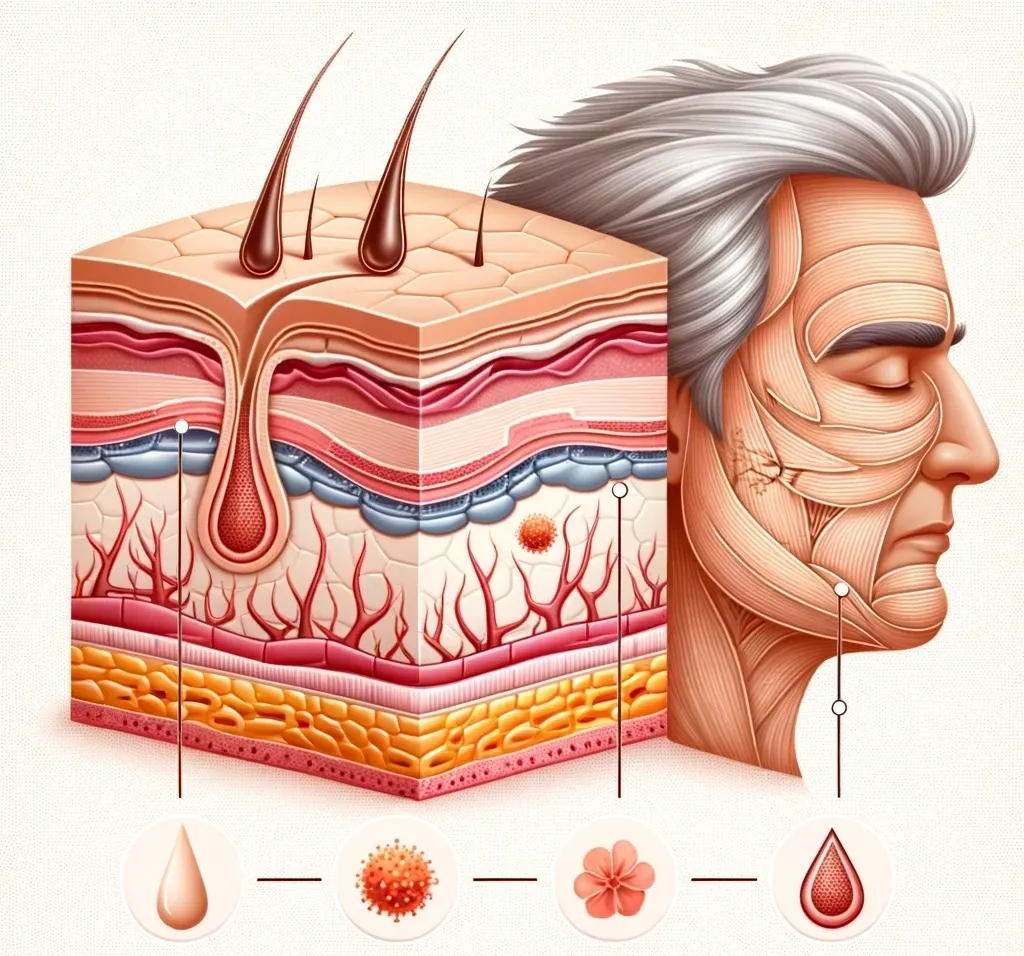
Aging is an inevitable biological process that progressively changes the skin’s structure and function. This includes a reduction in collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid, which are essential for skin strength, elasticity, and hydration.
- Reduced Collagen and Elastin: Collagen provides structural support, while elastin ensures flexibility. As we age, their production decreases, leading to sagging, loose, and wrinkled skin.
- Decreased Hyaluronic Acid: This substance hydrates the skin. Its reduction causes dryness, volume loss, and fine lines.
- Thinning Skin: Skin layers thin over time, losing their ability to repair effectively.
Genetic Factors
Genetics significantly influence skin type, collagen production, and aging speed. Some individuals experience wrinkles or sagging earlier due to genetic predispositions. Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome can also weaken skin structure.
Sun Damage (Photoaging)
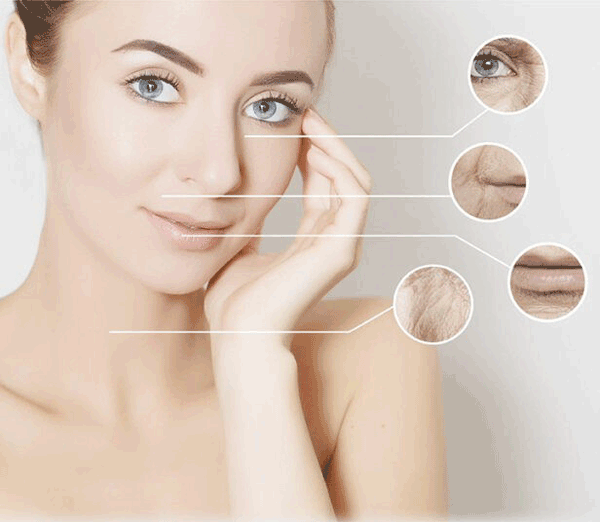
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays is a leading cause of premature skin aging, known as photoaging, with effects often more severe than natural aging.
- Collagen and Elastin Breakdown: UV rays degrade these proteins, causing wrinkles and sagging.
- Dark Spots (Lentigo or Melasma): Sun exposure increases melanin production, leading to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
- Dryness and Roughness: Long-term sun exposure reduces skin moisture, resulting in dry, rough texture.
Oxidative Stress and Free Radicals
Free radicals, unstable molecules, damage cells, proteins, and DNA. They are produced through bodily metabolism, but external factors like pollution, cigarette smoke, sunlight, and poor diet amplify their production.
- Cellular Damage: Free radicals impair skin cells and reduce collagen production, contributing to wrinkles and sagging.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during menopause, pregnancy, or severe stress, significantly affect skin health. Reduced levels of hormones like estrogen and testosterone lead to thinner skin, decreased collagen and elastin, and reduced moisture.
- Menopause: Lower estrogen levels cause volume loss and wrinkles.
- Hormonal Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): These can trigger acne and pigmentation changes.
Rapid Weight Loss
Sudden, significant weight loss can reduce subcutaneous fat, which supports skin structure, leading to sagging, especially in areas like the face, neck, and arms.
Unhealthy Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors can accelerate premature skin aging:
- Smoking: Reduces blood flow to the skin and damages collagen.
- Poor Diet: Processed foods, high sugar, and unhealthy fats cause inflammation and premature aging.
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake leads to dry, less elastic skin.
Chronic Stress
Persistent stress increases cortisol production, which reduces collagen and damages skin structure. It also exacerbates conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
Environmental Factors and Air Pollution
Air pollution, containing fine particles and harmful chemicals, penetrates the skin, causing inflammation, oxidative stress, and collagen breakdown. These contribute to wrinkles, dark spots, and sagging.
Improper Skincare
Failing to use appropriate skincare products, such as sunscreens, moisturizers, and antioxidants, accelerates aging. Using unsuitable products or over-cleansing can also harm the skin.